Why does one person become completely engrossed in learning everything about the Second World War while another embarks on globe-trotting adventures to explore new destinations and cultures? We all know the person who has a new hobby every week and the other one who is focused on one thing. And they are all curious.
Curiosity, far from being a simple concept, possesses dimensions as intricate as the human mind itself. Its exploration spans centuries, with roots extending back to the philosophical inquiries of Aristotle. While delving into antiquity might be tempting (I already ordered two books to explore the topic), let's fast forward to more recent investigations.
In 1890, William James, a prominent figure in American psychology, delved into the depths of human psychology in ‘The Principles of Psychology.’ In his book he proposed curiosity as an innate instinct propelling individuals toward knowledge and comprehension. He distinguished two types of curiosity:
Emotional Curiosity: This type of curiosity involves a fascination with new and unfamiliar stimuli, as well as a craving for exciting or stimulating experiences. Emotional curiosity may manifest as a general interest in exploring the world and seeking out new sensations, without necessarily focusing on acquiring factual knowledge or understanding.
Pursuit of Scientific Understanding: This form of curiosity is characterized by a thirst for empirical knowledge and a desire to comprehend the world around us. It involves asking questions, seeking explanations, and engaging in systematic inquiry to acquire factual knowledge and deepen one's understanding of phenomena.
Daniel Berlyne, in the 20th centry, expanded upon William James' groundwork. He conducted experimental investigations into curiosity's influencing factors, such as novelty, uncertainty, and conflict. By manipulating factors such as the predictability of outcomes or the availability of information, he investigated how uncertainty motivates individuals to seek out additional information and engage in exploratory behavior.
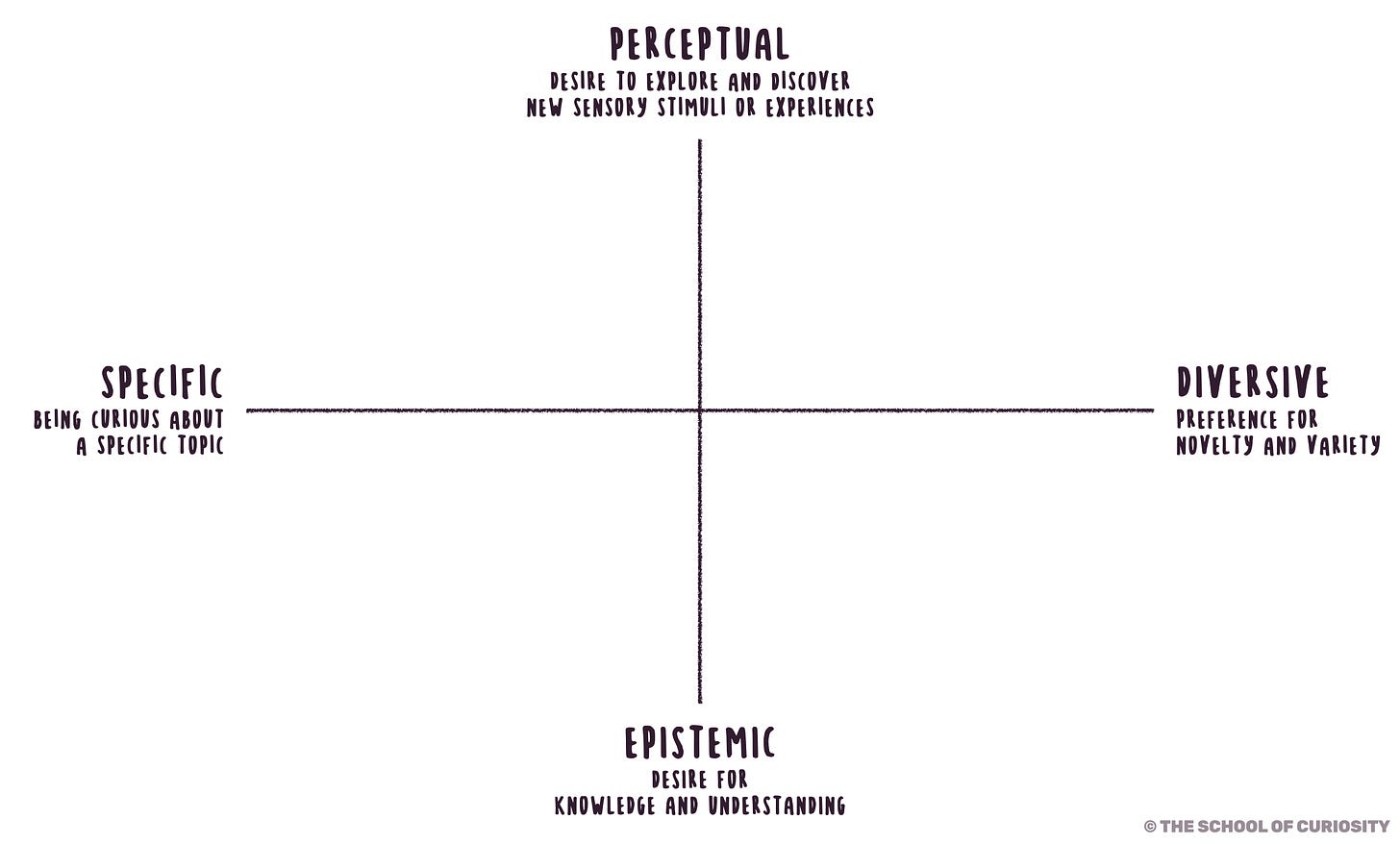
Berlyne conducted experiments to investigate the role of novelty in triggering curiosity. He exposed children to novel stimuli or situations and observed their reactions and exploratory behavior. In the end, Berlyne identified patterns shaping human and animal exploratory behavior. In his research he sought to develop a more nuanced understanding of curiosity. He proposed a two-axis model to explain his theory.
1. Epistemic curiosity vs Perceptual curiosity
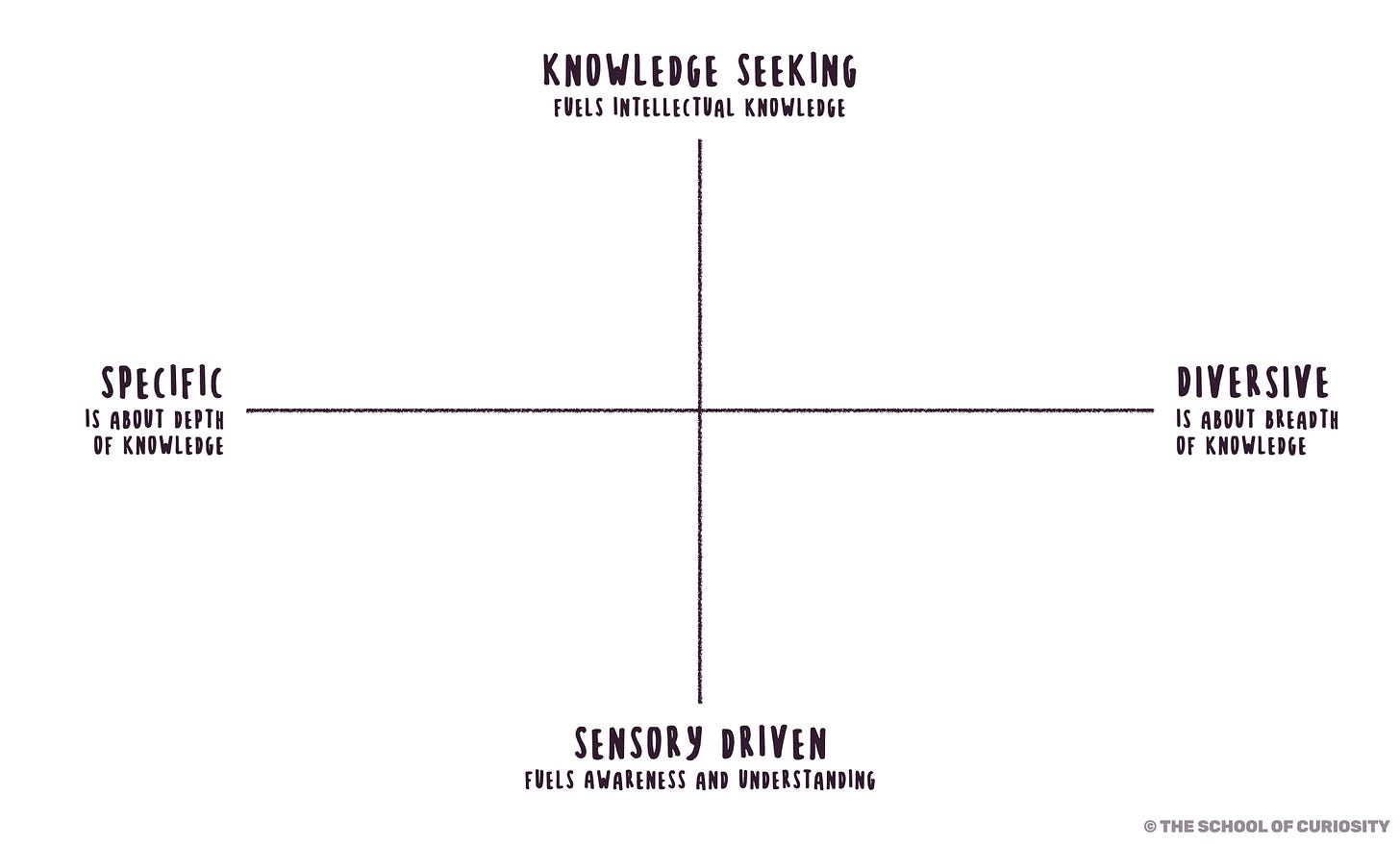
Along one axis, Berlyne differentiated between two types of curiosity: epistemic and perceptual curiosity. They are somewhat similar to the ones William James defined. Personally I like to describe them as knowledge-seeking and sensory-driven curiosity.
Knowledge-seeking curiosity fuels intellectual growth
Knowledge-seeking curiosity is characterized by a profound desire to understand the world around us. It is driven by a genuine thirst for knowledge and a deep-seated curiosity about the workings of the universe, society, and the human mind.
Knowledge-seeking curiosity is the engine that propels intellectual growth, deeply embedded in the academic world and the school system as we know it in Western society. From the towering intellects of Einstein to the ancient wisdom of Aristotle, this curiosity serves as a catalyst for intellectual development, igniting a lifelong quest for insight, ideas, and, above all, knowledge.
At its core, knowledge-seeking curiosity is driven by an innate desire to comprehend the world and unravel its mysteries. This quest for understanding spans a broad spectrum, from deciphering the workings of tectonic plates to unraveling the secrets of DNA. It can also manifest in simple yet profound acts, such as a child disassembling a radio or an adult delving into a podcast series on history or cycling. In each instance, there exists an inherent urge for comprehension and a thirst for knowledge.
Individuals propelled by this form of curiosity are marked by their insatiable hunger for knowledge and their unwavering pursuit of truth. They approach learning as a deeply enriching and rewarding journey, viewing each new piece of information as a stepping stone toward a greater understanding of the universe. They are avid learners, voracious readers, and passionate seekers of knowledge, embodying the essence of what universities strive to cultivate.
Knowledge-seeking curiosity fosters systematic inquiry and critical thinking. Rather than passively consuming information, curious individuals actively question, analyze, and evaluate the world around them. They approach problems with a spirit of curiosity and inquiry, exploring diverse perspectives, seeking evidence, and arriving at well-informed conclusions.
In essence, knowledge-seeking curiosity propels intellectual growth by inspiring individuals to push the boundaries of their understanding, question their assumptions, and pursue deeper insights into the world. It is through this relentless pursuit of knowledge that minds expand, intellects flourish, and human understanding advances.
Sensory-driven curiosity fuels awareness and understanding
Sensory-driven curiosity is primarily concerned with experiencing a deeper connection to the present moment, often evoking emotional responses, enhancing mindfulness, and building intuition. It is focused on new and unfamiliar stimuli, and seeking out experiences that evoke excitement, wonder, and emotional arousal.
Sensory-driven curiosity serves as a potent motivator for exploration and novelty-seeking, propelling individuals to engage the environment with their senses in profound ways. This form of curiosity manifests when encountering unfamiliar stimuli that pique one's interest, prompting a deeper investigation and exploration.
In natural settings, sensory-driven curiosity leads adventurers to explore uncharted trails, captivated by the allure of exotic flora and geological wonders. It inspires individuals to embrace challenges, such as bungee jumping, tasting a hot pepper or hiking treacherous landscapes, in pursuit of enriching sensory experiences. In urban environments, sensory-driven curiosity guides individuals to explore new neighborhoods, savor diverse cuisines, and immerse themselves in unique cultural events. It fuels a desire for tactile engagement with the world, opening doors to memorable experiences that broaden perspectives and deepen appreciation for diversity.
In the realms of arts, media, and technology, Sensory-driven curiosity drives individuals to seek out avant-garde exhibits, experimental music, and innovative technological advancements. It sparks creativity and innovation by encouraging individuals to dissect and analyze novel stimuli, leading to groundbreaking discoveries and advancements in various fields.
In essence, sensory-driven curiosity enriches our understanding of the world by encouraging physical exploration and engagement with diverse stimuli. It serves as a fundamental aspect of human nature, driving both everyday adventures and scientific discoveries, and fueling a relentless pursuit of exploration and novelty.
2. Specific vs Diversive curiosity
The type of curiosity is one thing, but there is another axis to be explored. And that is the axis of focus. Berlyne distinguished two types: specific and diversive.
Specific curiosity is about depth of knowledge
Specific curiosity is a focused and intense drive to explore and understand a particular subject deeply. It involves dedicating time and effort to unravel the complexities and nuances of a chosen topic, with individuals immersing themselves in research, study, and the quest for knowledge and expertise. This form of curiosity prioritizes depth over breadth, as individuals prefer delving deeply into a single topic rather than skimming the surface of multiple subjects. Mastery of violin play, culinary arts, in-depth knowledge of historical events like World War I, or a profound understanding of Japanese culture are prime examples of specific curiosity in action.
By embracing specific curiosity, individuals gain a profound understanding and appreciation of their chosen subject, enriching their lives and broadening their horizons. Whether through the pursuit of a creative skill, the exploration of historical events, or the study of diverse cultures, specific curiosity fuels a passionate commitment to learning and understanding, leading to personal growth and contributing to the collective body of knowledge in their chosen fields
Diversive curiosity is about breadth of knowledge
Diversive curiosity is a broad and exploratory drive to seek novelty, variety, and stimulation in various aspects of life. It encompasses a desire to experience new sensations, explore unfamiliar territories, and encounter different ideas and perspectives. Individuals driven by diversive curiosity thrive on the excitement of discovery and adventure, constantly seeking out new challenges and experiences to engage their senses and stimulate their minds.
Examples of diversive curiosity abound in everyday life, from traveling the unbeaten path (the real one, not the ones already explained online) and trying out new foods to exploring diverse hobbies. These individuals enjoy stepping out of their comfort zones, embracing opportunities for exploration and discovery, and immersing themselves in the richness of life's experiences. By embracing diversive curiosity, individuals not only satisfy their craving for novelty and variety but also cultivate a sense of openness, adaptability, and resilience in the face of uncertainty and change.
By proposing this two-axis model, Berlyne provided a more nuanced framework for understanding curiosity's complexity. It allows for a comprehensive examination of the various dimensions of curiosity, shedding light on its multifaceted nature and how different types of curiosity interact and influence behavior.
Turning the spotlight inward: cultivating balanced curiosity
This article is a starting point. A foundation for understanding the dimensions of curiosity in theory. But now, it’s time to turn the spotlight inward. Ask yourself: what type of curiosity do you focus on most? Are you diving deeply into a single subject while neglecting the thrill of the new? Or are you endlessly seeking novelty without grounding yourself in deeper understanding? True growth lies in finding balance between these dimensions and cultivating a more holistic approach to curiosity.
Curiosity flourishes when we resist the urge to confine ourselves to one type. The interplay between specific and diversive curiosity, as well as knowledge-seeking and sensory-driven exploration, drives creativity, innovation, and growth. By blending these forms of curiosity, we create a dynamic synergy: the deep understanding needed to master the familiar and the openness to embrace the unfamiliar.
It’s not just about the questions you ask but about the breadth and depth of your exploration. So, consider this a challenge: step back and evaluate your curiosity. Where does it thrive, and where does it falter? Because the true magic happens when we actively cultivate curiosity in all its dimensions, unlocking the full potential for discovery, growth, and transformation.